In September 1998, Roman Prokhorov and Igor Galaida (Moscow) passed all main underwater galleries of the cave up to the rock blockages and the length of underwater labyrinth of the cave increased by 500 m. to a new total of 2480 m.
SUMMARY OF THE KARST GEOLOGY
Physico-geographical position
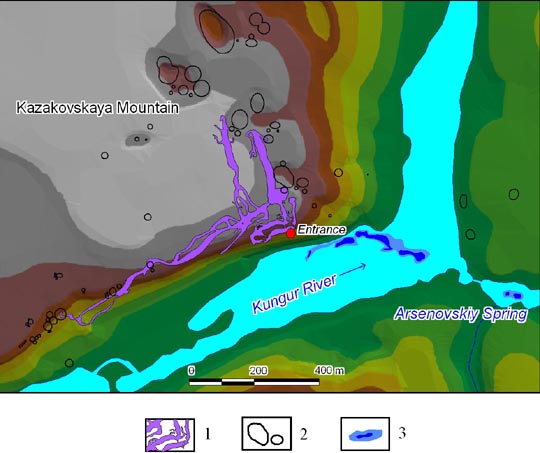
Ordinskaya Cave is located near the southwest end of the village of Orda in the Perm Region, on the eastern end of the Russian Plain. Kazakovskaya Mountain massif in which the cave in situated, presents a plateau-like upland, from the south, east and north embraced by the valley of Kungur River. The height of the massif above the water level in the river within cave development does not exceed 50 m. There are large karst sinkholes on the surface of the mountain, in one of which, located on the southern steep slope of the massif, the cave entrance is situated.
Geological Structure of the Massif
In structural-tectonic terms, the region around Ordinskaya Cave is situated on the eastern edge of the Eastern-European Platform and at the western wing of the Ufimskaya Swell Structure. In its arch, part of the Artinskian Limestones and Philippovskiy Horizon of the Kungurian are exposed and on its wings — the Irenskiy Gypsum Horizon. The structure has an asymmetric structure: the east wing is steep and narrow, whilst the western is flat and wide. The angles of incidence on the western wing change from 10° up to 1°. Two different strata take part in the geological structure of Kazakovskaya Mountain in which massif the cave is situated: the covering, consisting of karst-collapse sediments, and bedrocks of the Kungurian Stage of the Lower Permian. Karst-collapse sediments consist of clay, loams, detritus and debris of destroyed carbonate, less often — sulfate rocks. Downward in section they turn into Ol’khovskaya Breccia, presented by cemented debris of limestone and dolomite. Bedrocks are presented by sediments of the Irenskiy and Philippovskiy Horizons of the Kungurian Stage. Under the Ol’khovskaya Breccia there are destroyed from a surface gypsums and anhydrites of Shalashinskaya Layers (thickness is up to 15 m), which change downwards in section by carbonate rocks of the Nevolinskaya Layers (thickness is 8–12 m.), and then by gypsums and anhydrites of Ledyanopescherskaya Layers (thickness is 15–20 m.). The Ledyanopescherskaya Layers lie on dolomites and limestones of the Philippovskiy Horizon.
Hydrogeology and Karst
The Kungur River Valley was formed on the western border of the Ufimskoye Plateau, in a zone of dipping carbonate rocks of the Artinskian and Kungurian Stage under gypsums and anhydrites of the Irenskiy Horizon. Fractured-karst waters of the Philippovskiy-Artinskian water-bearing horizon, moving from east to the west along the bedding, unload here and flow into the gypsum-anhydrite strata. Evidence of this are the appearance of large karst springs along the border of the Ufimskoye Plateau, one of which (Arsenovskiy, with the mid-annual discharge of water about 300 1/sec) is located on the right bank of the Kungur River at about 700 m. to the east of the cave entrance. The linear zone of unloading of underground waters extends from the entrance of the cave in the direction of Arsenovskiy Spring, and can be seen in a channel of the Kungur River. Proof of the intensive karst processes along the border of the carbonate and sulphate rocks is evidenced by the extended (in meridional direction) series of large karst sinkholes on the surface of Kazakovskaya Mountain. Close to this border, the Kungur Ice Cave is situated — the largest gypsum cave of the Perm Region.
Speleo-Morphology
The cave entrance is situated on the steep southern slope of the mountain in a karst sinkhole of 15 m. in diameter and of 10 m. in depth, in the base of gypsum exposure. From the entrance, a talus of block-collapse and clay sediments extends down into the cave and continuing to «Crystal Hall» with a length of 30 m., width of 15 m. and height of up to 8 m. In the arch of the hall, gypsums and anhydrites of the Shalashinskaya Layer are exposed, and lower down — the limestones and dolomites of the Novolinskaya Layer. In northwest corner of the hall, at a depth of 21 m. from entrance, the «Ice Lake» is situated with its water level close to that of the Kungur River. The main passage of the cave turns to the left from the entrance hall and comes to the 50 m. long «Ice Palace Hall» which extends in a southwest direction, with dimensions of up to 15 m. in width and up to 7 m. height. In the right wall of the hall formed along the discharge joint, limestones and dolomites are exposed, and in a ceiling laid along the joints of bedding, — gypsum is exposed. The floor of the hall is covered with debris which fell from its ceiling. The amount of collapse-debris increases upon moving away from the entrance, the floor raises and at the end of a hall it is almost closed up with a ceiling. In the northeast part of a hall there is the «Main Lake» with an area of about 20 sq. m. At the end of the hall there are two passages in a block bulk which lead firstly to the distant «Warm Lake» with an area of 25 sq. m. and then to the last hall of the dry part of the cave — «Maximovich’s Hall».
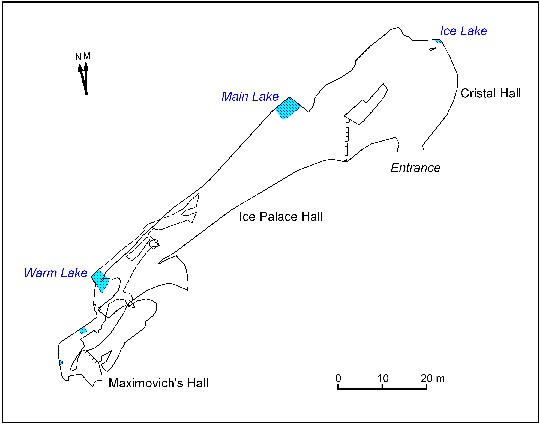
Fig. 2 Dry part ofOrdinskaya Cave.
Cave lakes are the entrances to the big underwater system of passages which was formed in the Ledyanopescherskaya Layers of gypsums and anhydrites of the Irenskiy Horizon of Kungurian Stage of Early Permian, situated below the level of underground waters. Undepwater passages we-re formed in a saturated zone of circulation due to arrival into a gypsum massif, aggressive in relation to gypsum underground waters from fractured limestones and dolomites of Phili-ppovskiy Horizon of Kungurian Stage, which are underlying gypsum-anhydrite strata. Slightly karstified Nevolinskaya limestone-dolomite Layers overlay the Ledyanopescherskaya Layers, the lower layers of which are also below the level of underground waters and prevents from collapse of arches of underwater galleries, which reach into the last passages with significant cross sections. In similar conditions, probably, the main galleries of Kungur Ice Cave were formed which dried up after the lowering of the local base-level of erosion.
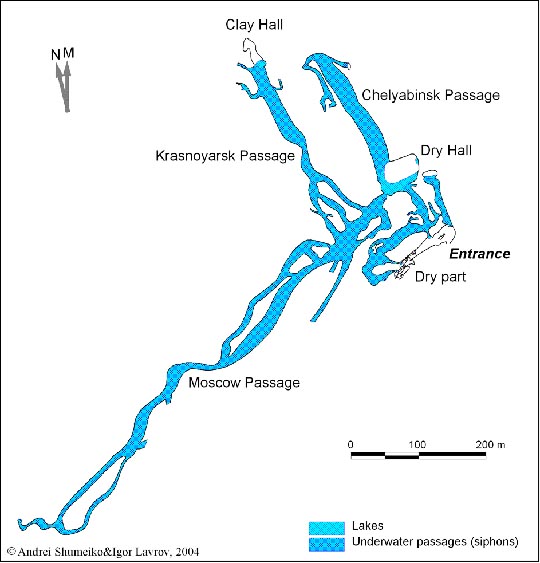
Fig. 3 Plan of Ordinskaya Cave.
The area of Ordinskaya Cave is 34000 sq. m.
REFERENCES
Lavrov I A, 1999: Ordinskaya Cave. In: Caves, # 25–26. Perm (Russia), pp. 47–52
Maximovich G A, 1969: Caves of Gypsum Karst. In: Caves, #7 (8). Perm (Russia), pp. 5–29